
The art of photoshop can sometimes be a lifesaver. Imagine being able to restore heavily damaged family photos that are truly precious to you? While it is easy to use shortcuts the best results often come from meticulous care. And the following restorations of 'unrestorable' photographs will make you gasp:
A woman’s only photo of herself as a young child, and the only image of her grandparents
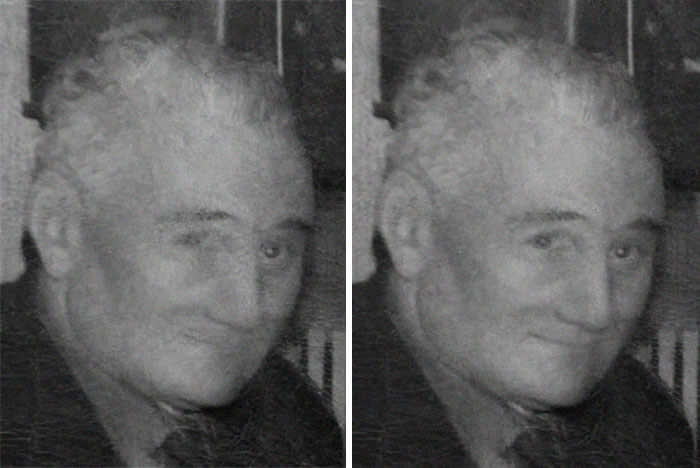







"The original image is on the left. On the right is the image after reducing the contrast adjacent to the tears and cracks, then filling the cracks using sampling of adjacent pixels. This can be done using tools in Photoshop like “content-aware” fill or the healing brush. However, in areas where accurate detail is critical (such as faces), I prefer to do this step manually by eye, as it keeps the highest number of undamaged pixels intact."
The image on the left shows the layer of sampled greys used to fill the cracks and tears. On the right, the green indicates the areas of missing emulsion (data). As you can see, it’s not as much damage as you might suspect. When filling the cracks, I work in a separate layer and fill only the areas of missing emulsion. I do not paint over undamaged or intact areas of the photo, and I do not blend the fill into surrounding areas.
The image on the left shows the layer of sampled greys used to fill the cracks and tears. On the right, the green indicates the areas of missing emulsion (data). As you can see, it’s not as much damage as you might suspect. When filling the cracks, I work in a separate layer and fill only the areas of missing emulsion. I do not paint over undamaged or intact areas of the photo, and I do not blend the fill into surrounding areas.
Much of the loss is in areas that are what I call “non-critical”, meaning there’s not much in the way of identifiable features. Carefully dodged/burned transitions in these areas will flesh out the face. The yellow areas are where critical detail has been lost. These areas contribute significantly to a person’s appearance. Loss in these areas can be difficult to restore. But again, the areas are fairly small in relation to the size of the head.
Another thing worth paying attention to is the “big picture” areas of damage. Scanning a damaged photo will often leave highlights and shadows that can be misleading. The dotted lines indicate where the large tears were, and where I need to pay attention to shading, distinguising what’s in the photo vs. shadows caused by the scanner lamp. Knowledge of anatomy becomes critical at this point, so you can balance shading in a way that’s consisten with the shape of the skull and flesh. I usually squint or blur (then undo) so I can see the shape better.
The image on the left is what I believe to be a pretty accurate reconstruction of the gentleman in the photo. I arrived at this using sampling techniques (manual and digital), and blending using the smallest dodge/burn brushes. From there, I created details in the features that were both generic and suitable within the context of other features (right). This is where knowledge of anatomy and illustration skills help in restoration. You may not always be able to achieve “historical” accuracy, but the end result will be much closer to the actual appearance than using other repair techniques. Save your shortcuts and tricks for areas of an image that are not as critical as eyes, mouths, noses. Working pixel by pixel is tedious, but the results are can be rewarding."
Removed tubes from a baby photo


Repair of the only photo of the client’s mother from her youth
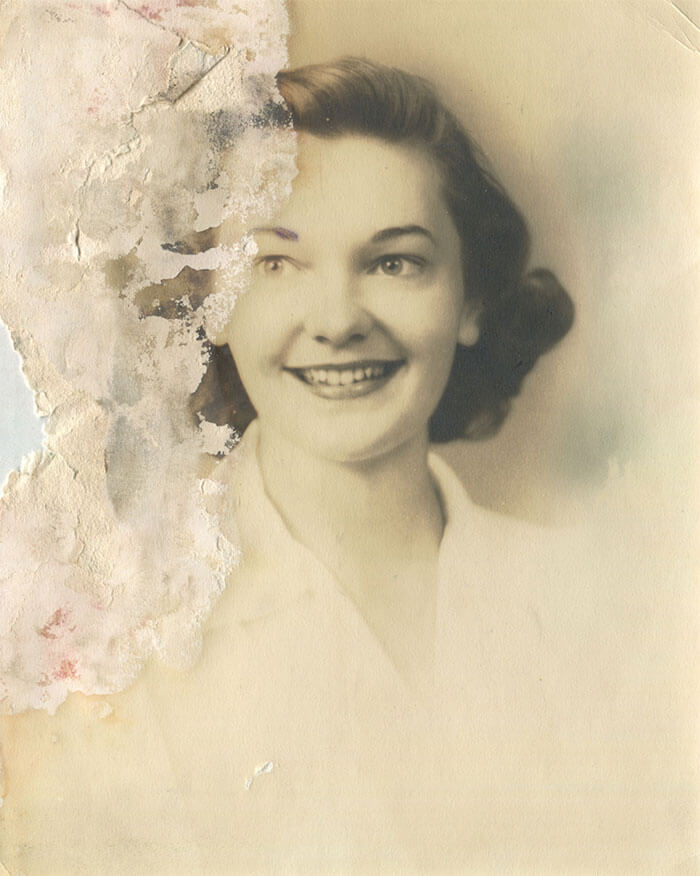

The only photo a man had of his mother, who died when he was born


An early 20th century family photo


A cat destroyed this favorite photo of a beloved uncle


Repaired emulsion loss from the only photo of the subject as a child


Restoration of a vintage photo with a large shadow



Only photo of an ancestor as a child


Repair and colorization of a long lost relative
















COMMENTS